What is a Heart Attack?
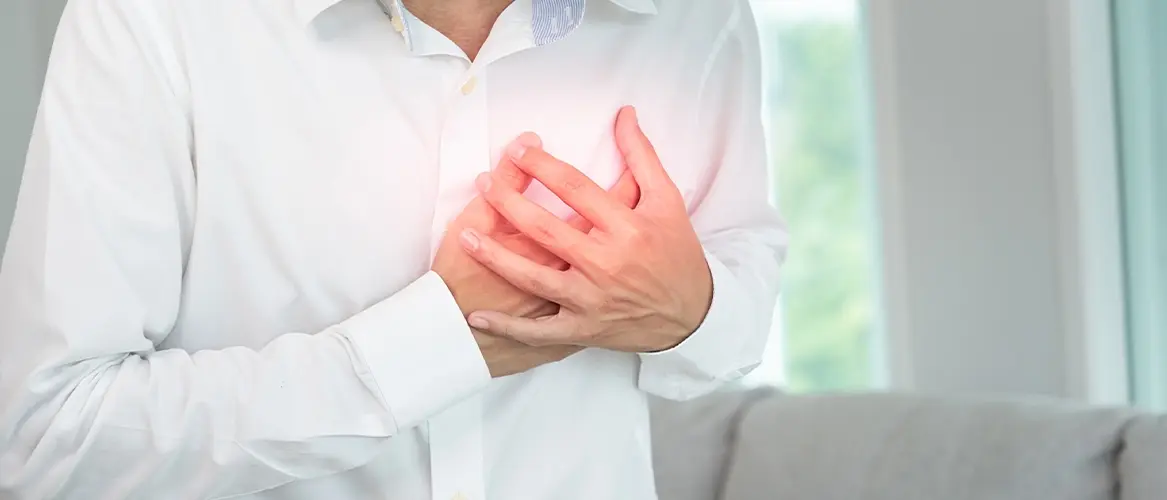
Heart attack, known in medicine as "myocardial infarction," is one of the most feared disorders among the public. Many people ask, "What is a heart attack?". While looking for an answer to the question, many of them ask, "Why does a heart attack happen?". A heart attack is a condition in which the coronary vessels that feed the heart are blocked, resulting in damage to the muscle tissue of the heart. The interrupted blood flow causes severe damage to the heart. For this reason, it is necessary to open the vessels and prevent the loss of heart tissue with correct and timely intervention.
Heart Attack Symptoms
A heart attack can have many symptoms, mild or severe. Therefore, with the answers to the question "What are the symptoms of a heart attack?" the most basic symptoms can be understood. The primary symptom felt by a person having a heart attack is severe chest pain. It can be said that a weight collapses behind the rib cage, and there is a pressing pain. This type of pain does not decrease or increase with breathing or movement. The pain may also spread to the jaw, back, shoulder, arm, abdomen, or neck. In some cases, right arm numbness can even be a sign of a heart attack. In some cases, left hand and finger numbness can be associated with a heart attack.
It is also wondered about how long the symptoms of a heart attack last. In general, the pain of the attack does not go away without necessary intervention.
Heart attack symptoms include nausea and vomiting, sudden cold sweats, dizziness, distressed general condition, fatigue, shortness of breath, and heart rhythm disorder. Contrary to what is commonly known, the symptoms of a heart attack may not constantly occur in the form of severe and sudden chest pain. Some people can have a silent and hidden heart attack (especially those with diabetes) without apparent symptoms. Heart attack symptoms in men may be different than in women. According to research by the American Heart Association, back or jaw pain, shortness of breath, vomiting, and nausea are more common in men who have a heart attack. On the other hand, heart attack symptoms in women are more focused on the rib cage. In men, this starts with pressure on the rib cage and spreads to the arm.
How Heart Attack Occurs
The main reason underlying the heart attack is the clot formed due to the rupture of the plaques formed due to cholesterol accumulating on the vessel wall. As a result of this situation, the blood supply of the heart muscle cannot be met due to occlusion of the arteries. Cardiac muscle cells begin to die, and the heart muscle loses its function in the occluded area. It means heart muscle cells are lost every second. Therefore, early intervention in a heart attack is vital.
Causes of Heart Attack
The most important point among the causes of heart attack is the accumulation of cholesterol plaques on the arterial wall (atherosclerosis). As a result, hardening of the vessel walls will occur, and the inner artery channel will be narrowed. If the narrowed vessels cannot provide enough blood flow to the body, enough oxygenated blood cannot reach the heart muscle. Other answers to the question about the "causes of a heart attack" include an unhealthy diet, excessive stress, genetic predisposition, or smoking as primary causes.
Many people have a buildup of fat or plaque in the coronary arteries that goes silently for years. While the factors added on top of each other cause the veins to become clogged over time, smoking, in particular, plays a role as an accelerating effect in this regard. The risk of heart attack is three times higher, regardless of smoking men and women.
Another cause of heart attack is the high rate of LDL, which is defined as bad cholesterol. To keep this type of cholesterol at a minimum, foods such as processed meat (salami, sausage), red meat, mussels, squid, fried foods, offal, cream, mayonnaise, full-fat products, and butter should be avoided.
Having diabetes can also increase the risk of a heart attack. Studies show that people with diabetes are more likely to have heart attacks. Diabetes destroys the flexibility of the vessel walls, increases the level of coagulation in the blood, and causes the cells on the inner surface of the vessels to be damaged more easily. In addition to these, when conditions such as lack of physical activity and unhealthy diet are added, the risk of heart attack arises.
Other causes of heart attack can be listed as follows:
- High blood pressure (hypertension),
- Obesity,
- Lack of physical activity,
- Congenital heart diseases,
- Age (>55 in women, >45 in men).
How Long Does a Heart Attack Last?
Burning and tightness in the chest, paleness, sweating, and shortness of breath are among the first signs of a heart attack. These symptoms can continue for hours if the heart vessel is entirely occluded; it is not very likely that the pain will go away without the necessary intervention. If the boat is not entirely blocked, if the vessel is narrowing, it manifests as severe chest pain for 10-15 minutes. Those who wonder how long a heart attack will last should follow these symptoms and take the necessary measures correctly and quickly from the moment the symptoms are seen.
What should you do in case of a heart attack?
The question of what to do during a heart attack is an essential issue for many people, both for themselves and for their relatives. Chest pain, which is the first and most vital sign of a heart attack, starts as pressure and burning and then spreads to the neck and arm. Cold sweating begins on the back and forehead. Sometimes, it can be seen as a heart attack accompanied by severe symptoms and sometimes as mild discomfort. In the meantime, the pain increases with movement and decreases with rest but does not go away completely. It can last over half an hour and may be accompanied by cold sweats and nausea. Therefore, mild or severe chest pain should always be considered.
At the time of a heart attack, we race against time. It is necessary to reach a health unit as soon as possible. A person who has a heart attack should never go to the hospital by themselves and should avoid doing activities that require more oxygen, such as climbing stairs. The first precautions you can take for yourself and those around you who have had a heart attack may be:
- The first thing to do when one of the heart attack symptoms starts is to call for professional help. So 112 should be called immediately.
- Call the ambulance and your relatives if you are alone and close to your phone.
- Loosen/open the collars of your clothes, such as ties or shirts.
- Since a heart attack requires first aid, seek help if you have an experienced person with you. If the person has not received first aid training, do not let them interfere with you and ask them to call the ambulance. No matter how close you are to the person having a heart attack, you should not intervene if you do not have first aid training.
- Open windows and doors to fill the environment with plenty of oxygen.
- If you have a heart attack while driving, pull over immediately and seek help.
Will a patient with a stent have a heart attack again?
After a heart attack, the occluded artery(s) are opened by using a stent by the doctor, who decides to perform angiography to open the occluded vessel. Stent placement, which is seen as one of the first interventions for a patient who has a heart attack, should be performed by a specialist doctor in a hospital setting. Stent insertion, defined as a surgical intervention, carries some risks, just like other surgeries. In addition, there is a risk that some vessels may not receive stent after stent placement. This brings the question, "Can a patient with a stent have a heart attack again?" to minds. As stated, if the stent is not received, if occlusion or narrowing of the vessel occurs again, the patient may experience a second heart attack. For this reason, the drugs given after the stent insertion should be used regularly, the recommendations of the specialist doctor should be followed, and the necessary checkups should not be skipped.

 Let Us Call You
Let Us Call You