What is Dialysis?
Dialysis is purifying blood from harmful waste products when the kidneys cannot perform their normal functions. Dialysis removes excess water, electrolytes, and other toxins from the body. The kidneys filter the blood and expel harmful waste pmroducts and extra fluids from the body through the urinary system.
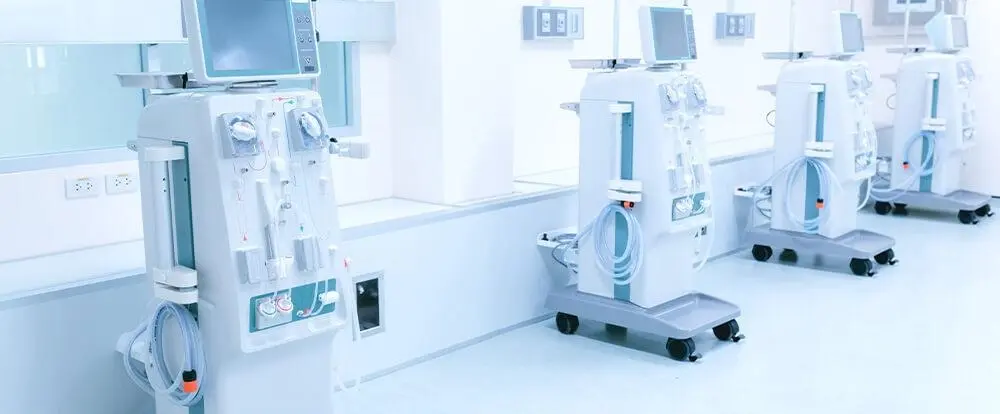
However, some health problems or diseases can cause the kidneys to function abnormally or fail. In this case, dialysis filters the blood through a dialysis machine and eliminates harmful substances from the body. Dialysis can be performed in two ways: Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Hemodialysis is a process in which the blood is purified using a dialysis machine.
Peritoneal dialysis, on the other hand, is performed with a catheter placed into the abdominal cavity. During this process, a unique solution (dialysate) is injected into the abdominal cavity, which absorbs excess water and waste products from the body and is eliminated.
Why is Dialysis Needed?
The most common reason for needing dialysis is the inability of the kidneys to function adequately. The kidneys filter the blood and eliminate harmful substances and excess fluids from the body through the urinary system. However, in some cases, the kidneys' functions can be insufficient or completely stopped. In these situations, dialysis may be necessary.
Some common reasons why dialysis may be needed are:
- Chronic kidney disease: The gradual loss of kidney function over time.
- Diabetes: Diabetes can cause damage to the kidneys.
- Hypertension (high blood pressure): High blood pressure can cause damage to the kidneys.
- Polycystic kidney disease: Polycystic kidney disease is a genetic disease that causes masses to form in the kidneys and can lead to a gradual loss of kidney function.
- Certain medications:Certain medications can harm the kidneys and lead to kidney failure. In addition to these factors, dialysis may also be necessary in emergencies such as acute kidney failure. In these cases, the kidneys are rapidly damaged, and dialysis is needed to remove waste products and excess fluid from the body.
In addition to these factors, dialysis may also be necessary in emergency situations such as acute kidney failure. In these cases, the kidneys are rapidly damaged, and dialysis is needed to remove waste products and excess fluid from the body.
How Does Dialysis Work?
Dialysis is a treatment method used to eliminate harmful substances and excess water from the body when the kidneys are not functioning correctly. It is a filtration process that cleanses the blood and removes unnecessary fluid from the body. There are two types of dialysis: hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
Hemodialysis is the most common method used for dialysis treatment. The patient's blood is passed through a dialysis machine to filter out harmful substances, excess water, and electrolytes. The filtered blood is then returned to the patient's body. This process usually takes around 4 hours and is performed 2-3 times weekly.
Peritoneal dialysis is a different type of dialysis treatment. A unique solution is introduced into the patient's abdomen during this process. The solution passes through the patient's peritoneal membrane and collects in the abdominal cavity, removing harmful substances and excess water. Peritoneal dialysis can be done at home without being attached to a dialysis machine and is usually performed 4-5 times daily.
Both dialysis methods remove harmful substances and excess water from the patient's blood. Hemodialysis may be challenging for some patients, as it requires them to stay in a dialysis unit in the hospital, while peritoneal dialysis may be a more comfortable option. Dialysis treatment is personalized based on the patient's medical condition and needs.
What is done in a Dialysis Unit?
Dialysis units are specialized centers where dialysis patients receive treatment and the dialysis process is carried out. In these units, healthcare professionals monitor patients' treatment, and treatment plans are adjusted as needed. Before and after the dialysis process, the following procedures are carried out in dialysis units:
- Patient evaluation: An assessment is made of patients who apply to the dialysis unit regarding their medical history and current condition. This assessment helps determine appropriate treatment plans.
- Blood tests : Dialysis patients' blood tests are conducted before and after dialysis. Blood tests are essential for monitoring kidney function and the effectiveness of dialysis treatment.
- Dialysis process : Dialysis patients are treated by connecting to a dialysis machine. Hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, or other dialysis methods may be used. The blood is cleaned during this process, and excess water is removed from the body.
- Medication therapy :Dialysis patients may take medications during or after the dialysis process to treat other medical conditions, such as lowering blood pressure, correcting anemia, stopping bone loss, or preventing blood from clotting in the lines.
- Nutritional support : Dialysis patients' nutritional needs are monitored in the dialysis unit, and dietitians prepare unique diet plans.
- Psychosocial support : Dialysis units also try to meet patients' psychosocial needs. For this purpose, patients can be provided psychological support and social services.
- Dialysis units provide all necessary facilities to ensure patients' comfort and the best possible treatment process.

 Let Us Call You
Let Us Call You